Formelsamling matematik
Den här formelsamlingen kommer från Wikibooks. Formelsamlingen behöver förenklas genom att några delar tas bort så att eleverna känner igen sig.
Räknelagar
| [math]\displaystyle{ a+b=b+a\,\! }[/math] | (kommutativa lagen under addition) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a\cdot b=b\cdot a\,\! }[/math] | (kommutativa lagen under multiplikation) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b)+c=a+(b+c)\,\! }[/math] | (associativa lagen under addition) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a\cdot b)\cdot c=a\cdot (b\cdot c)\,\! }[/math] | (associativa lagen under multiplikation) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a\cdot (b+c)=a\cdot b+a\cdot c\,\! }[/math] | (distributiva lagen) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a+c=b+c \ \Leftrightarrow \ a=b\,\! }[/math] | (annulleringslagen under addition) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a \cdot c=b \cdot c \ \Leftrightarrow \ a=b \quad om \ c\ne 0\,\! }[/math] | (annulleringslagen under multiplikation) |
Bråkregler
| [math]\displaystyle{ a\cdot \frac{b}{c}=\frac{a}{1} \cdot \frac{b}{c}=\frac{ab}{c} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ c\neq 0 }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{b}\cdot\frac{c}{d}=\frac{ac}{bd} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ b\neq 0, d\neq 0 }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{b}\Big/\frac{c}{d}=\frac{\frac{a}{b}}{\frac{c}{d}}=\frac{a}{b}\cdot\frac{d}{c}=\frac{a}{b}\frac{d}{c}=\frac{ad}{bc} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ b\neq 0, c\neq 0, d\neq 0 }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{b} + \frac{c}{d} = \frac{ad}{bd} + \frac{bc}{bd} = \frac{ad+bc}{bd} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ b\neq 0, d\neq 0 }[/math] |
Parentesregler
| [math]\displaystyle{ a+(-b)=a-b\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a \cdot b=ab\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a-(-b)=a+b\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a \cdot (-b)=a(-b)=-ab\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (-a) \cdot (-b)=(-a)(-b)=ab\,\! }[/math] |
Algebra
Låt [math]\displaystyle{ a,b,c\in \mathbb{R} }[/math] och [math]\displaystyle{ m,n\in \mathbb{Z} }[/math].
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b)^2=a^2+2ab+b^2\,\! }[/math] | (första kvadreringsregeln) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a-b)^2=a^2-2ab+b^2\,\! }[/math] | (andra kvadreringsregeln) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2\,\! }[/math] | (konjugatregeln) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b)^3=a^3+3a^2b+3ab^2+b^3\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a-b)^3=a^3-3a^2b+3ab^2-b^3\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^3+b^3=(a+b)(a^2-ab+b^2)\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^3-b^3=(a-b)(a^2+ab+b^2)\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ n! = (1\cdot 2\cdot 3\cdot ...\cdot n) = \prod_{k=1}^n k }[/math] | (fakultet) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b)^n= \sum_{k=0}^{n} {n\choose k}a^{n-k}b^k = \sum_{k=0}^{n} \frac{n!}{k!(n-k)!} a^{n-k}b^k }[/math] | (binomialteoremet) |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a_1+a_2+...+a_m)^n= \sum_{k_1+k_2+...+k_m=n}^{} \frac{n!}{{k_1}!{k_2}! ... {k_m}!} a_1^{k_1}a_2^{k_2} ... a_m^{k_m} }[/math] | (multinomialteoremet) |
Kvadratkomplettering
- [math]\displaystyle{ x^2 + px = x^2 + px + (\frac{p}{2})^2 - (\frac{p}{2})^2 = (x - \frac{p}{2})^2 - (\frac{p}{2})^2 }[/math]
Förstagradsekvationen
| [math]\displaystyle{ ax+b=0\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ a \ne 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ x=- \frac {b}{a}\,\! }[/math] |
Andragradsekvationen
Rötterna till andragradsekvationen på formen [math]\displaystyle{ x^2+px+q=0 }[/math] ges av:
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1 = -\frac{p}{2} + \sqrt{\left(\frac{p}{2}\right)^2-q} \quad och \quad x_2 = -\frac{p}{2} - \sqrt{\left(\frac{p}{2}\right)^2-q} }[/math]
då gäller
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1 + x_2 = -p\,\! }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1 \cdot x_2 = q\,\! }[/math]
Kvadratrötter
För [math]\displaystyle{ a\ge 0,\ b \ge 0,\ c \gt 0 }[/math]:
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt {a} \cdot \sqrt{a}=a\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt {a} \cdot \sqrt{b}= \sqrt {ab}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ b \sqrt {a}= \sqrt {b^2 a}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac {\sqrt {a}}{\sqrt {c}}= \sqrt{\frac {a}{c}}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac {a}{\sqrt {c}}= \frac {a \sqrt {c}}{c}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt[n]{ab}=\sqrt[n]{a}\sqrt[n]{b}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt[n]{\frac{a}{c}}=\frac{\sqrt[n]{a}}{\sqrt[n]{c}}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt[m]{\sqrt[n]{a}}=\sqrt[mn]{a}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a\sqrt[n]{b}=\sqrt[n]{a^n b}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt[m]{\sqrt[n]{a}}=\sqrt[n]{\sqrt[m]{a}}\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt[nq]{a^{mq}}=\sqrt[n]{a^m}\,\! }[/math] |
Potensregler
| [math]\displaystyle{ 1^n=1\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^n= \underbrace{a \cdot a \cdot \ldots \cdot a}_{n} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^1 =a\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^0=1\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ a \ne 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^{-n}=\frac{1}{a^n}\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ a \ne 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^{1/2}= \sqrt{a}\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^{m/n}=(a^m)^{1/n}= \sqrt[n]{a^m}\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ m,\ n\ \gt 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^m \cdot a^n=a^{m+n}\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a^m}{a^n}=a^{m-n}\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ a \ne 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (ab)^m = a^m\cdot b^m\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \left( \frac{a}{b} \right)^m=\frac{a^m}{b^m}\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ b \ne 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ (a^m)^n=a^{m\cdot n}=(a^n)^m\,\! }[/math] |
Logaritmer
För [math]\displaystyle{ y\gt 0,\ a\gt 0,\ a\ne 1 }[/math]:
| [math]\displaystyle{ y=10^x\Leftrightarrow x=\log_{10}\ y=\lg\ y\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ y=a^x\Leftrightarrow x=\log_{a}\ y\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ y=e^x\Leftrightarrow x=\ln\ y\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \ln\ y=\ln\ 10\cdot \lg\ y\approx 2,3026\ \lg\ y\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \lg\ y=\lg\ e\cdot \ln\ y\approx 0,4343\ \ln\ y\,\! }[/math] |
Logaritmlagar
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^{\log_a x}=x\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \log (ab)=\log a+\log b\,\! }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ a\gt 0\ och\ b\gt 0\,\! }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \log \frac{a}{b}=\log a-\log b\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \log_a a^n=n\log a\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \log_a\sqrt[n]{a}=\frac{1}{n}\log a\,\! }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ a^{\frac{\log b}{\log a}}=b\,\! }[/math] |
Formelsamlingen kommer ursprungligen från Wikibooks
Geometri
Trigonometri

En rätvinklig triangel är en triangel där en av vinklarna är 90 grader. Sidan som är motsatt den räta vinkeln kallas hypotenusa och de två övriga sidorna kallas katetrar.
- Sinusfunktionens värde för en vinkel är kvoten mellan motsatta sidan till vinkeln och hypotenusan:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sin A = \frac{a}{c} }[/math]
- Kosingsfunktionens värde för en vinkel är kvoten mellan närliggande sidan till vinkeln och hypotenusan:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \cos A = \frac{b}{c} }[/math]
- Tangensfunktionens värde för en vinkel är kvoten mellan motstående och närliggande sidas längd:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \tan A = \frac{a}{b} = \frac{\sin A}{\cos A} }[/math]
Triangelsatserna
Areasatsen
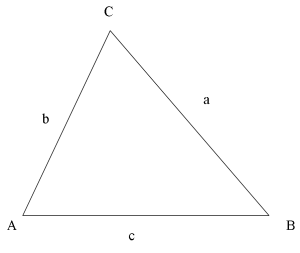 [math]\displaystyle{ \mbox{Area} = \frac{1}{2}a b\sin C. }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \mbox{Area} = \frac{1}{2}a b\sin C. }[/math]
Sinussatsen
 [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C} }[/math]